Generating Correlation Heat Maps in Seaborn

It’s Getting Hot In Here.
Let’s revisit a previous post, where we had been working with Abalone data from the UCI Machine Learning Repository.
Previously, we had generated a scatter matrix to look for linear correlations, here’s a refresher of our results:
Scatter Matrix - Abalone Data
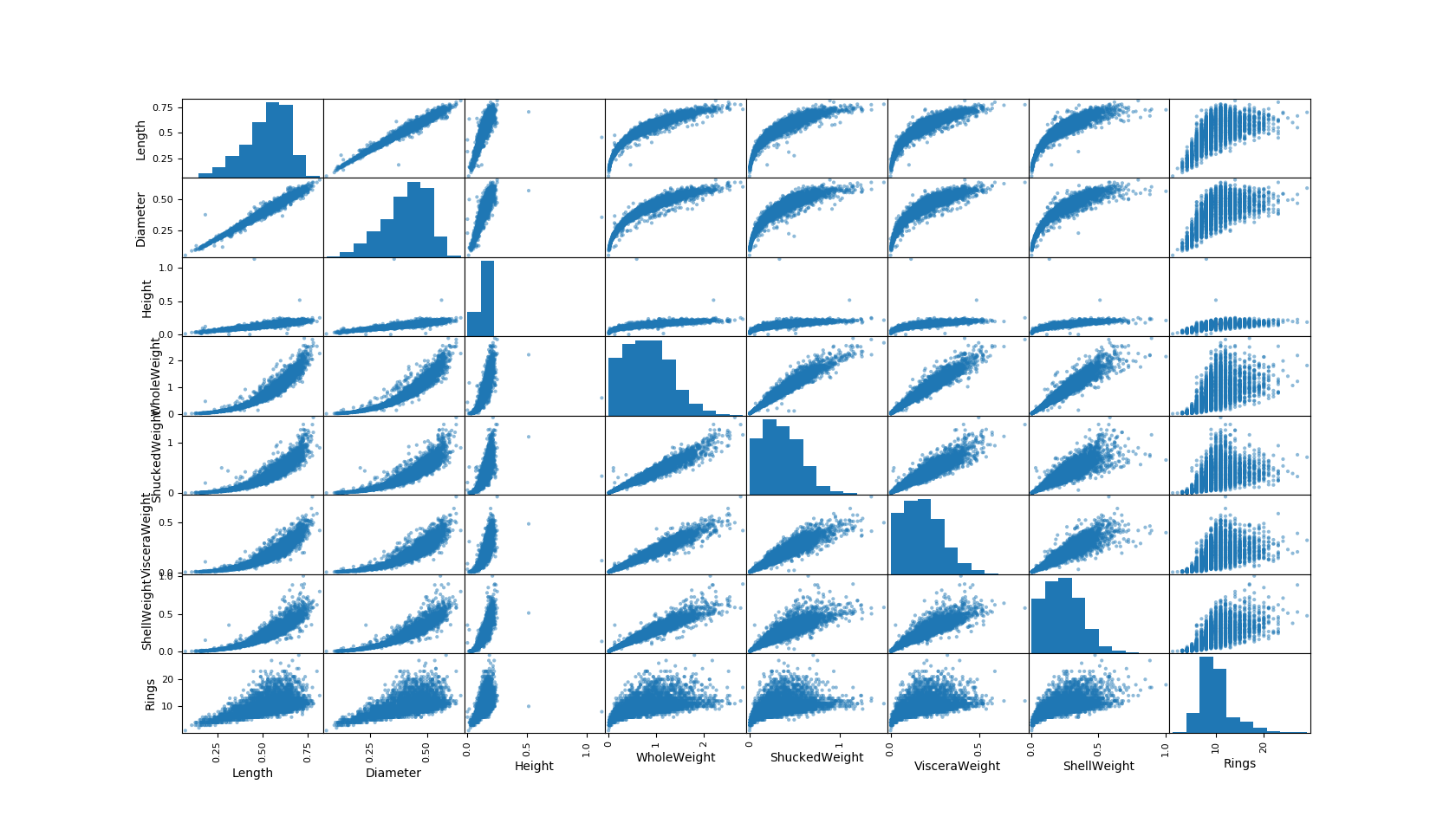
This time, let’s use the same dataset to generate a Seaborn Heat Map of correlation coefficients.
We’ll be utilizing the following Python modules
Imports
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
I’ve modularized the previous data call, which will give us a Pandas DataFrame of the online data.
Grab All The Data
def getDF(data_url, columns):
#retrieve data from url, create dataframe, return it
data = pd.read_csv(data_url, names=columns)
return data
Next, let’s build our heat map! It’s important to note that we will be creating our own color gradient map, with high correlations displayed in increasing red shades, and lower correlations trending into the blue hues.
We will also add our correlation values inside the graph itself, displaying floating numbers in each category.
Seaborn Heat Map
def heatMap(df):
#Create Correlation df
corr = df.corr()
#Plot figsize
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
#Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
#Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f")
#Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
#Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
#show plot
plt.show()
Visualize It
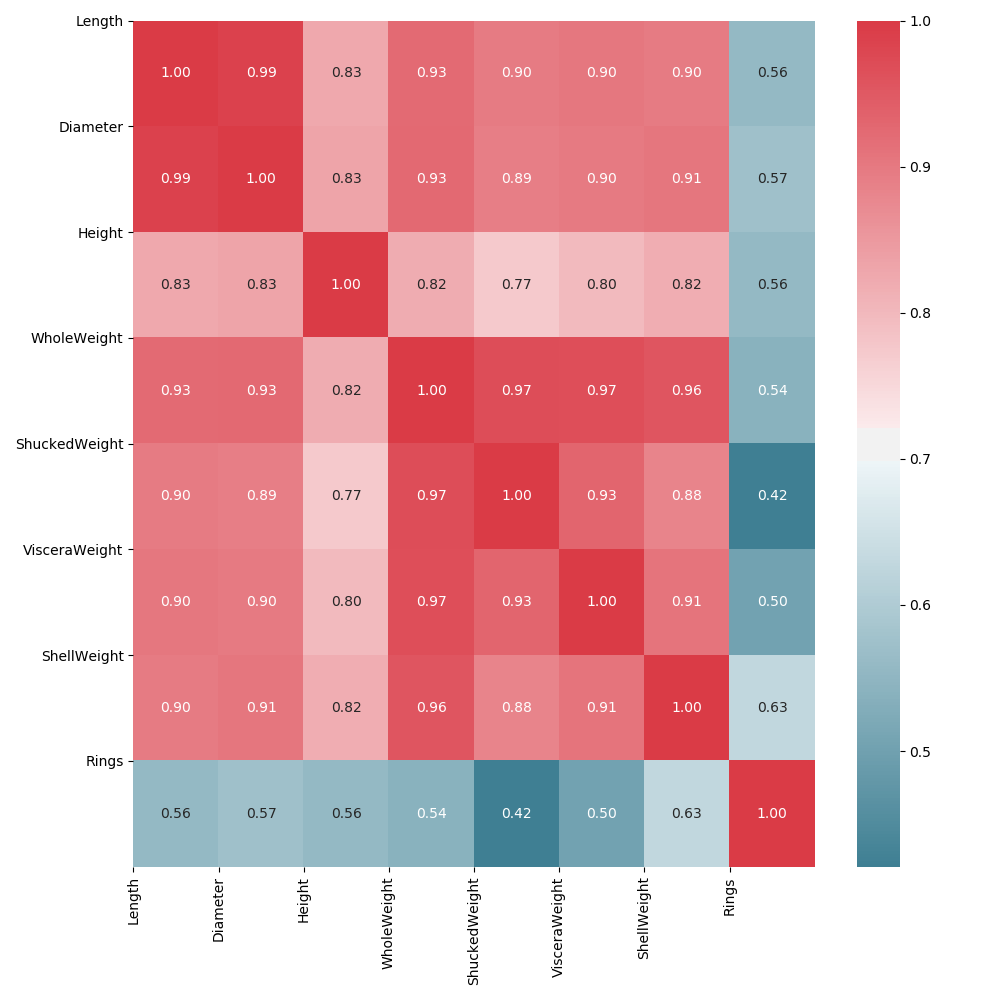
Awesome! However, we can do better. The diagonal plane mirrors itself on either side, with both redundant results AND self to self correlations, which we should drop.
Toggling Our Plot, Apply Mask Parameter
Let’s alter our previous code a little, by adding in a ‘mirror’ parameter that will allow us to drop our redundant mappings.
If the user enters a second paramenter, ‘mirror’, as ‘False’, we will generate half the visualization as we did previously.
def heatMap(df, mirror):
# Create Correlation df
corr = df.corr()
# Plot figsize
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
# Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
if mirror == True:
#Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f")
#Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
#Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
#show plot
else:
# Drop self-correlations
dropSelf = np.zeros_like(corr)
dropSelf[np.triu_indices_from(dropSelf)] = True
# Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
# Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f", mask=dropSelf)
# Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
# Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
# show plot
plt.show()
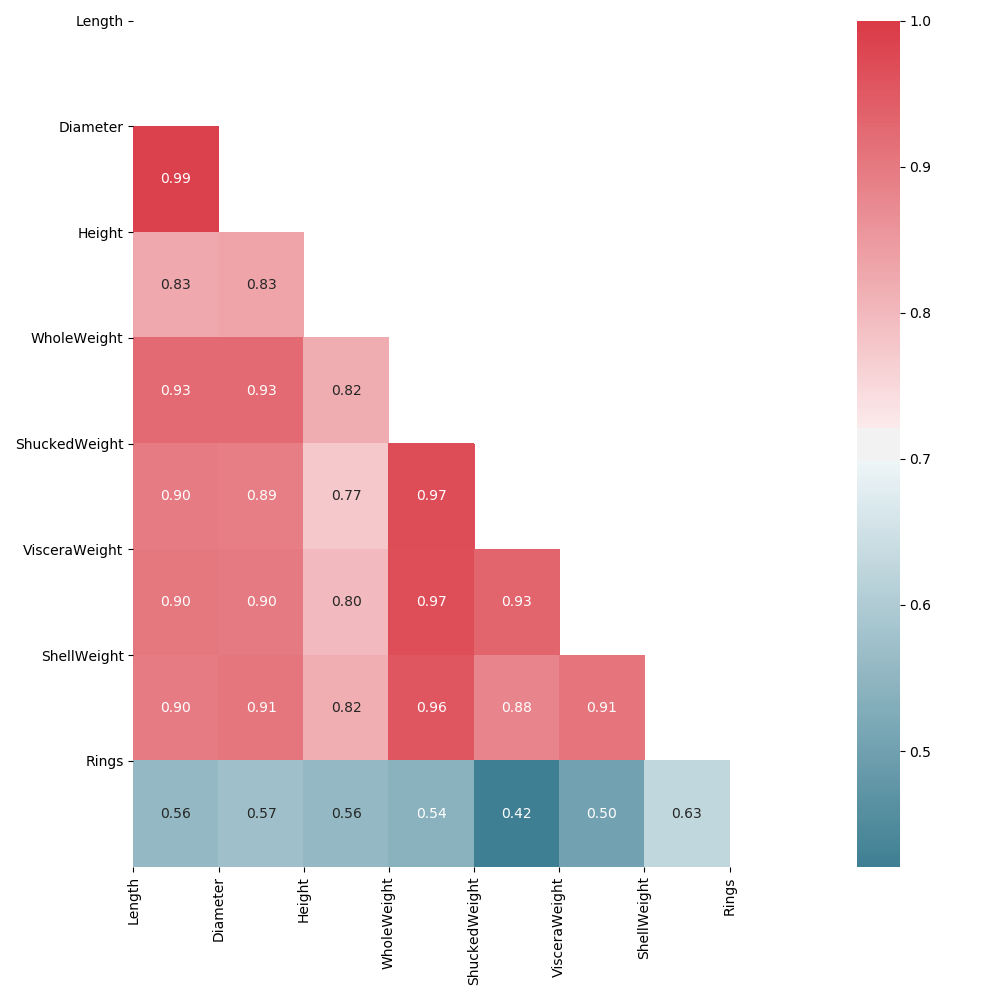
Much better! We’ve dropped a substantial amount of redundant information that only served to act as distractive noise. Now we can focus on the relationships with ease.
Code Summary
Part I
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
def getDF(data_url, columns):
#retrieve data from url, create dataframe, return it
data = pd.read_csv(data_url, names=columns)
return data
def heatMap(df):
#Create Correlation df
corr = df.corr()
#Plot figsize
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
#Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
#Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f")
#Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
#Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
#show plot
plt.show()
Part II
def halfHeatMap(df, mirror):
# Create Correlation df
corr = df.corr()
# Plot figsize
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
# Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
if mirror == True:
#Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f")
#Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
#Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
#show plot
else:
# Drop self-correlations
dropSelf = np.zeros_like(corr)
dropSelf[np.triu_indices_from(dropSelf)] = True
# Generate Color Map
colormap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
# Generate Heat Map, allow annotations and place floats in map
sns.heatmap(corr, cmap=colormap, annot=True, fmt=".2f", mask=dropSelf)
# Apply xticks
plt.xticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns);
# Apply yticks
plt.yticks(range(len(corr.columns)), corr.columns)
# show plot
plt.show()
